Output gap
The GDP gap or the output gap is the difference between potential GDP and actual GDP or actual output. The calculation for the output gap is Y*–Y where Y* is actual output and Y is potential output. If this calculation yields a positive number it is called an inflationary gap and indicates the growth of aggregate demand is outpacing the growth of aggregate supply—possibly creating inflation; if the calculation yields a negative number it is called a recessionary gap—possibly signifying deflation. [1]
The percentage GDP gap is the actual GDP minus the potential GDP divided by the potential GDP.
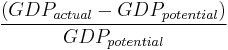 .
.
Contents |
Okun's Law: The relationship between output and unemployment
Okun's Law is based on regression analysis of US data that shows a correlation between unemployment and GDP. Okun's law can be stated as: For every 1% increase in cyclical unemployment (actual unemployment - natural rate of unemployment), GDP will decrease by β%.
%Output gap = -β x %Cyclical unemployment
This can also be expressed as:
(Y-Y*) / Y* = -β(u-ū)
where:
- Y is actual output
- Y* is potential output
- u is actual unemployment
- ū is the natural rate of unemployment
- β is a constant derived from regression show the link between deviations from natural output & natural unemployment.
References
- ^ Richard G. Lipsey and Alec Chrystal. Economics. Oxford University Press. 11th edition. January 2007. p. 423.